Best Carbon Fiber 3D Printers
Carbon fiber is primarily used in industrial applications due to its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, stiffness, and resistance to temperature and chemical exposure. These make it ideal for industries such as aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing, where performance and durability are critical. Carbon fiber components are significantly lighter than their metal counterparts, yet they maintain comparable strength, which is crucial for reducing weight in aircraft and high-performance vehicles. Additionally, carbon fiber’s resistance to corrosion and fatigue enhances the longevity and reliability of parts exposed to harsh environments and continuous stress. This makes it invaluable for producing robust tools, jigs, fixtures, and functional prototypes that can endure rigorous mechanical testing and operational demands. In addition to our list of the best carbon fiber 3D printers, this article also discusses what carbon fiber is and how to 3D print with this material to get the best results. First, these models made our list:
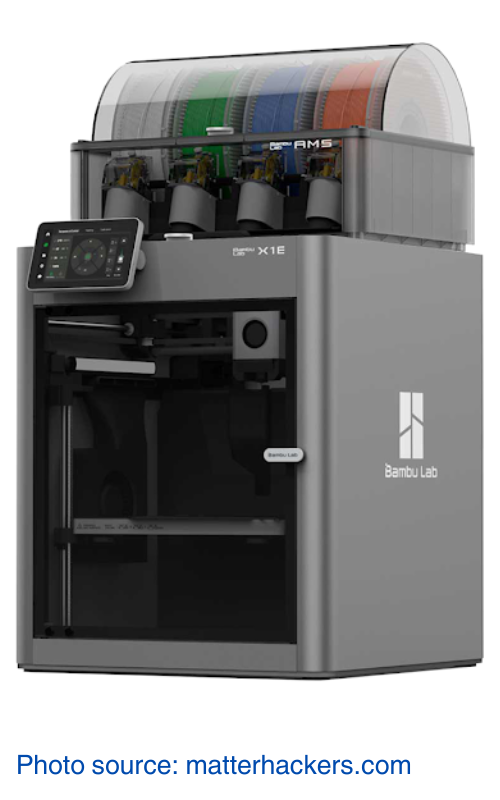
1. Bambu Lab X1E

Why it’s Top Notch:
- 256 x 256 x 256 mm Print Volume
- High precision with 50-micron layer resolution
- Dual extruder system with independent print heads
- Automated bed leveling and calibration
- Advanced cooling system
- User-friendly touchscreen interface
- Wide material compatibility including carbon fiber-reinforced filaments
The Bambu Lab X1E is a high-precision 3D printer designed to deliver outstanding print quality with a layer resolution of 50 microns. Its dual extruder system features independent print heads, allowing for complex, multi-material prints, including carbon fiber-reinforced filaments. The automated bed leveling and calibration ensure that the printing process is smooth and hassle-free. The advanced cooling system maintains optimal printing temperatures, essential for handling carbon fiber materials effectively. The X1E can handle high-performance materials such as PPA-CF/GF and PPS, ensuring exceptional dimensional stability and mechanical properties.
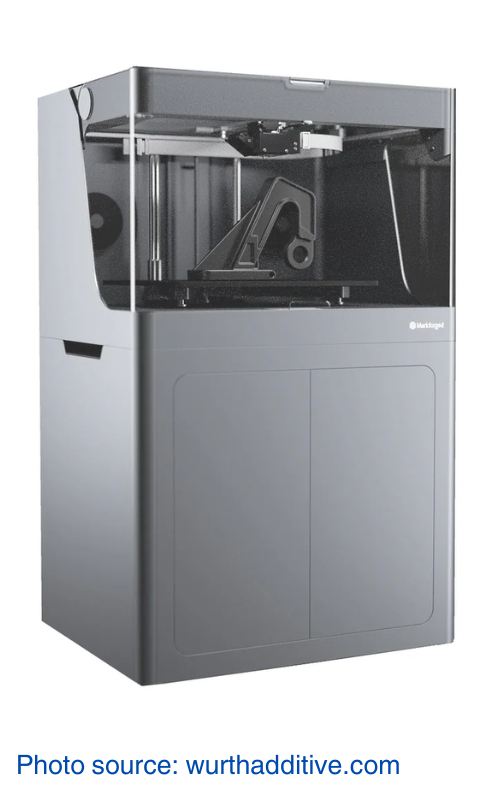
2. Markforged X7 Gen2

Why it’s Top Notch:
- Industrial-grade continuous carbon fiber reinforcement
- High precision with a resolution of 50 microns
- Large build volume of 330 x 270 x 200 mm
- Advanced cloud-based Eiger software
- Integrated laser micrometer for in-process inspection
The Markforged X7 Gen2 is designed for industrial-grade performance, with a continuous carbon fiber reinforcement that significantly enhances the strength and durability of printed parts. Its high precision and accuracy make it suitable for producing complex geometries and high-performance components. The large build volume accommodates bigger projects, while advanced software integration with Eiger streamlines the printing process, providing real-time monitoring and adjustments. Built with robust construction, the X7 Gen2 is capable of handling requirements of industrial applications, making it a reliable choice for manufacturing and prototyping.
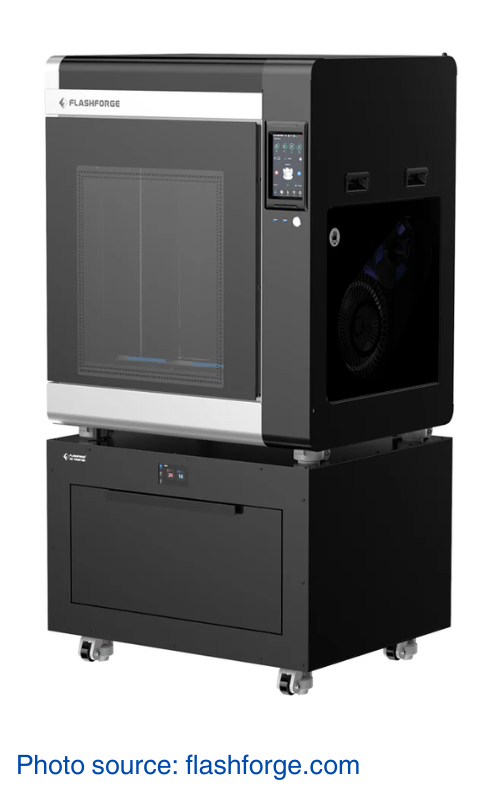
3. FlashForge Creator 4

Why it’s Top Notch:
- Interchangeable Independent Dual Extruder System (IIDEX)
- Large build volume: 400 x 350 x 500 mm
- High-temperature capabilities: Extruder-HS up to 360°C, Extruder-HT up to 320°C
- Temperature controlled heated printing chamber up to 65°C
- Intelligent Filament Management System
- Advanced touchscreen interface and built-in HD camera
The FlashForge Creator 4 is a commercial-grade 3D printer designed for industrial applications. Its Interchangeable Independent Dual Extruder System (IIDEX) allows for high-quality, oozing-free prints and efficient mass production. The large build volume of 400 x 350 x 500 mm accommodates sizable projects, while the high-temperature extruders (HS up to 360°C and HT up to 320°C) support a wide range of engineering materials, including carbon fiber composites. The temperature-controlled heated chamber maintains a consistent environment up to 65°C, enhancing dimensional accuracy and reducing thermal contraction. Additionally, the Intelligent Filament Management System ensures optimal printing conditions by automatically adjusting temperatures based on the material in use.
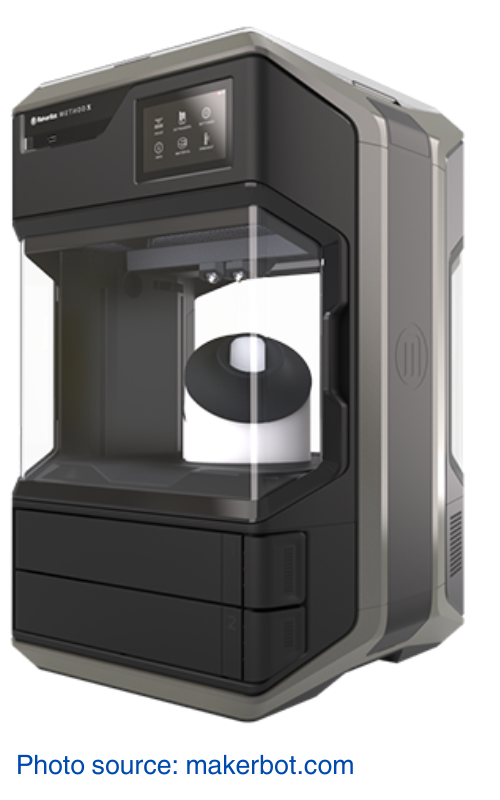
4. MakerBot Method X

Why it’s Top Notch:
- Patented VECT™ 110 Thermal Regulation system
- Dual performance extruders
- Circulating heated chamber up to 100°C
- SmartAssist material loading
- 5″ full-color capacitive touch screen
- CloudPrint™ for remote access
The MakerBot Method X is designed to bring industrial-grade 3D printing to the desktop. With its patented VECT™ 110 Thermal Regulation system, it ensures parts are stronger and more accurate by maintaining an even temperature throughout the build chamber. The dual performance extruders allow for high-quality prints with a variety of materials, including carbon fiber composites. The circulating heated chamber, capable of reaching up to 100°C, reduces warping and ensures consistent print quality from the first layer to the last. The SmartAssist material loading system simplifies the process of changing filaments, while the 5″ touchscreen and CloudPrint™ provide intuitive controls and remote access.
3D Printing with Carbon Fiber
Carbon fiber 3D printing allows for the creation of strong functional prototypes capable of withstanding rigorous mechanical testing, as well as final products like manufacturing jigs and fixtures. FDM machines are the most accessible entry point for carbon fiber 3D printing, although they are not the only option. Selective laser sintering (SLS) using carbon-fiber-infused nylon powder is another method, but FDM 3D printing remains the most economical and versatile choice for many businesses. This guide focuses on the top desktop- and benchtop-sized carbon fiber 3D printers.
What is Continuous and Chopped?
Carbon fiber-reinforced filaments come in various forms, including chopped carbon fiber, continuous carbon fiber (CCF), and continuous fiber co-extrusion (CFC). These materials are rapidly becoming viable replacements for molded carbon fiber and metal parts across numerous applications. But what is chopped and continuous carbon fiber? Chopped carbon fiber filaments contain short carbon fiber particles embedded within a base polymer like nylon or PEEK. These fibers align with the print direction during extrusion, enhancing the strength and stiffness of the final print. Typically, these filaments contain around 20% carbon fiber by weight, providing significant reinforcement while maintaining ease of printing.
Continuous carbon fiber (CCF) printing, on the other hand, involves laying down a continuous strand of carbon fiber alongside another material, usually through dual extruding nozzles. This method produces parts with superior strength and a more consistent load distribution, ideal for applications requiring targeted reinforcement.
Managing Carbon Fiber for Optimal 3D Printing
Carbon fiber material can be tricky to print with, so many printers offer features designed to address these points. For example, since carbon-fiber-infused filament is abrasive and the carbon fibers can lead to frequent nozzle clogging, affecting the smooth flow of filament, printers that manage carbon fiber material the best have a hot end that can maintain a high temperature consistently for a long time. The higher print temperatures put additional stress on the hot end, which can be balanced with a heated bed and an enclosure to prevent temperature fluctuations. A full enclosure isn’t strictly necessary, but consistent heat is the goal.
Bed adhesion can also be a problem, requiring specialized build surfaces to help prevent warping, and features such as precise bed leveling are important. Most critical, though, is a print profile of speed, temperature, and layer height tuned specifically to carbon fiber.
For Best Results
Achieving the best results with carbon fiber filaments requires careful management of several factors:
1. High Extruder Temperature: Carbon fiber-reinforced materials need a much higher extruder temperature, typically around 260°C or above. Ensure your 3D printer can reach these temperatures to avoid print failures.
2. Hardened Steel Nozzle: The abrasive nature of carbon fibers can quickly wear down standard brass nozzles. Upgrading to a hardened steel nozzle is essential to handle the abrasive material, though it may require a higher extruder temperature due to lower thermal conductivity.
3. Larger Diameter Nozzle: Using a nozzle with a larger diameter (0.5 mm or above) helps prevent clogs and reduces the risk of filament snapping, especially around tight corners or sharp turns.
4. Lower Print Speed: Reducing the print speed by about 50% allows the extruder to manage the carbon fiber filament more effectively, minimizing clogs and improving print quality.
5. Minimize Retraction: Adjusting your slicer settings to reduce or eliminate retraction distance can further reduce the risk of clogs, ensuring a smoother printing process.
Proprietary Materials
Some carbon fiber 3D printers use proprietary materials available only through the manufacturer. For instance, the Markforged Mark Two can print with continuous carbon fiber, Onyx (a nylon mixed with chopped carbon fiber), fiberglass, and Kevlar. The Anisoprint offers flexibility with continuous carbon fiber and basalt fiber, catering to different reinforcement needs.
By understanding the properties and managing the specific requirements of carbon fiber filaments, you can maximize the quality and strength of your 3D prints, harnessing the full potential of this advanced material.
Conclusion
The Bambu Lab X1E, Markforged X7 Gen2, FlashForge Creator 4-S, and MakerBot Method X each have their ability to effectively use carbon fiber as a material in 3D printing. These printers are equipped with features that handle the unique challenges of carbon fiber, such as high-temperature capabilities, advanced cooling systems, and big build volumes. Their precision and reliability make them excellent choices for producing strong, lightweight parts for various industrial applications. Each of the models ensures that carbon fiber 3D printing is accessible, efficient, and highly effective.




Comments are closed.